Ingredients & Formulation
Ingredient Spotlight: Lanolin and Plant-Based Alternatives for Natural Hydration
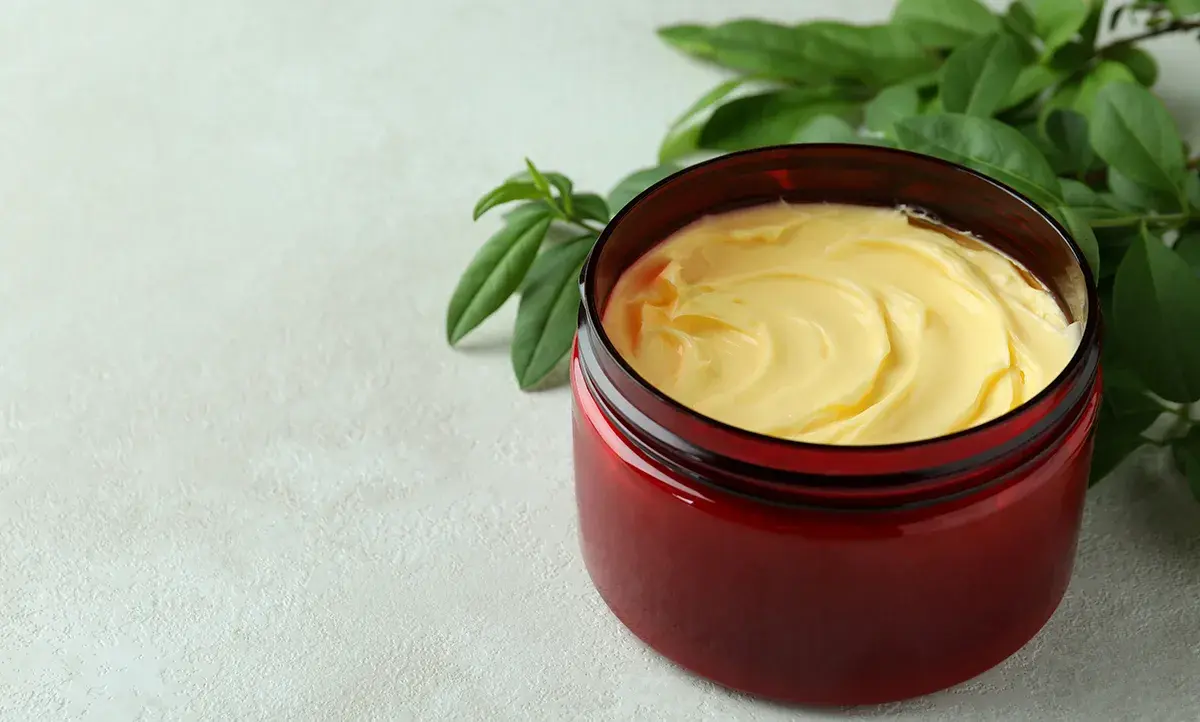

Lanolin, a natural ingredient derived from sheep’s wool, has been a staple in cosmetics for centuries, known for its exceptional moisturizing properties. It is used in a wide range of products, including lotions, creams, and balms, for body care, lip care, and more. The global lanolin market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% from 2024 to 2030, largely driven by consumer preference for natural and sustainable ingredients.
Despite its long-standing use, lanolin has faced challenges due to concerns about allergenicity and its animal-derived nature. These issues have led to the development of plant-based alternatives. Although some reports on lanolin’s allergenic effects are controversial, dermatologist Albert Kligman, M.D., even called lanolin allergy a myth. However, while lanolin can be certified cruelty-free, it is not considered vegan, which has prompted the rise of plant-based options.
Ingredient Spotlight: Lanolin and Plant-Based Alternatives for Natural Hydration, lanolin’s unique composition and properties have made it a popular choice in skincare, but its animal source and potential for allergic reactions have spurred the search for viable substitutes. Lanolin is composed mainly of esters, diesters, and hydroxy esters of aliphatic alcohols/sterols, giving it a thick, viscous consistency. It forms a protective barrier on the skin, preventing moisture loss, and is known to absorb up to 400% of its weight in water, making it highly effective as both an occlusive and humectant moisturizer.
Lanolin is extracted through a variety of methods, including solvent extraction of wool fleece, followed by refining processes that remove impurities and improve its color and odor. The refined lanolin is pale, ointment-like, and often treated with antioxidants to prevent oxidation and color darkening. These processes ensure that lanolin remains suitable for use in cosmetics and pharmaceutical applications.
Ingredient Spotlight: Lanolin and Plant-Based Alternatives for Natural Hydration, despite its benefits, lanolin is not without controversy, particularly regarding its allergenic potential. The Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) panel has reviewed lanolin’s safety multiple times, and while it is considered a weak sensitizer, the risk is minimal, especially when the ingredient is ultra-refined. As a result, lanolin and its derivatives are still regarded as safe for use in cosmetics.
However, for those seeking alternatives, several plant-based options have been developed. These alternatives aim to replicate lanolin’s water absorption, emulsifying capability, and skin-conditioning benefits. While these plant-based ingredients may not fully mimic lanolin’s unique properties, they offer promising options for consumers looking for vegan or non-animal-derived moisturizers. The search for effective lanolin replacements continues as demand for sustainable, plant-based ingredients grows in the cosmetics industry.